Authentication token manipulation error usually occurs when a user tries to change his password in Linux, but something goes wrong. This can be caused by various reasons, such as incorrect password file permissions or insufficient user rights.
Why does the error occur?
Translated literally, this error means that the password management utility passwd cannot manipulate a token. By token here we mean the hash of the password you specified. This can result from an inability to write a new hash to the configuration file because:
- the program does not have permissions to write to the
/etc/shadowfile; - the file system is mounted in read-only mode;
- file system corruption;
- there is no free space on the disk;
- an incorrect authentication module is used.
Next, let's see how to fix each of these problems to clear the error.
How to fix the error?
To fix this error, you can try the following steps:
- Try changing the password using the
"passwd" command with superuser(sudo) privileges. For example,sudo passwd username - Check the permissions of the password files
(/etc/passwd and /etc/shadow). Make sure they have the correct permissions (usually 644 for/etc/passwdand 640 for/etc/shadow). - If you are using a SELinux-enabled file system, make sure that SELinux does not block access to password files
- If you are using an ACL-enabled file system, make sure that permissions are set correctly
- If the error still occurs, try restarting the computer and trying to change the password again.
If none of the above help, the problem may be a more serious problem with the file system or user account, in which case it is worth contacting a professional for further troubleshooting.
Access rights
An error in the utility may occur if the permissions on the /etc/shadow file, where passwords are stored, are set incorrectly.
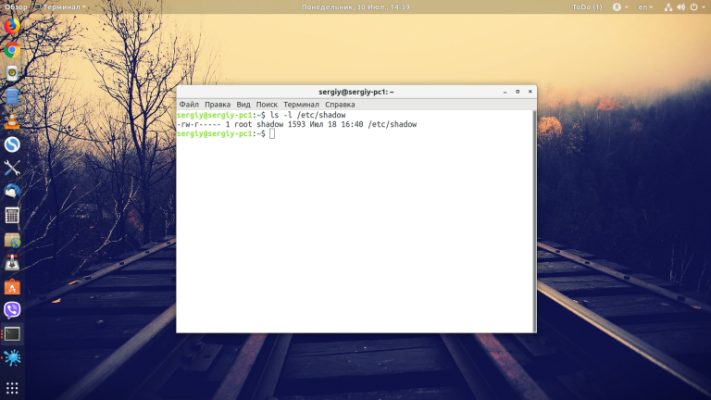
Check the current permissions with the command:
ls -l /etc/shadowYou should have read and write set as in the snapshot, if not, run a command like this:
sudo chmod 0640 /etc/shadowRead-only file system
If you booted into Ubuntu recovery mode or a similar mode of another distribution, the file system will be in read-only mode by default, so the utility will not be able to write anything. To remount it for writing, use:
sudo mount -o remount,rw /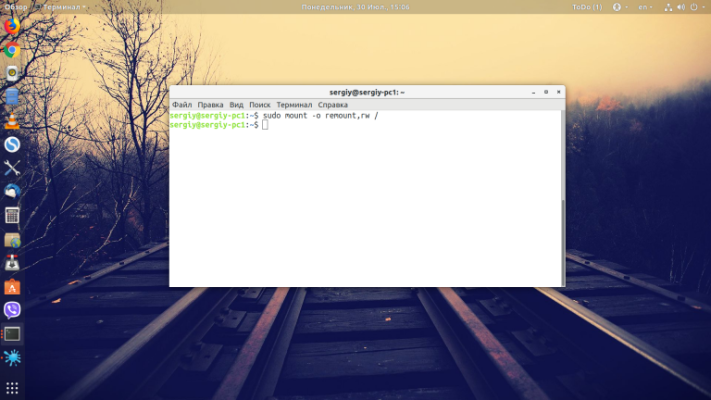
Authentication Modules
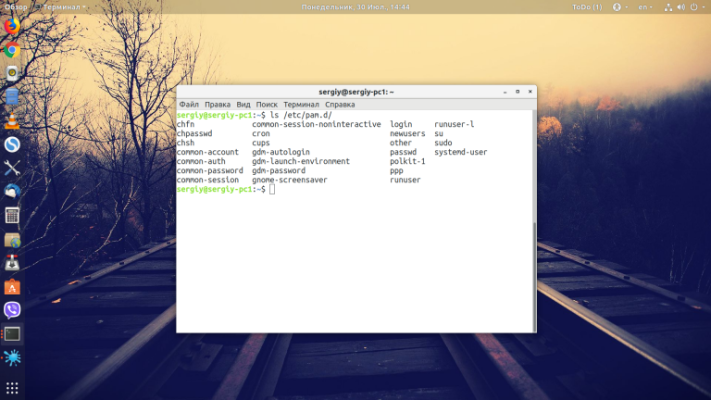
Another reason could be that the authentication modules are misconfigured and the utility is unable to save the password. Available modules can be viewed with the command:
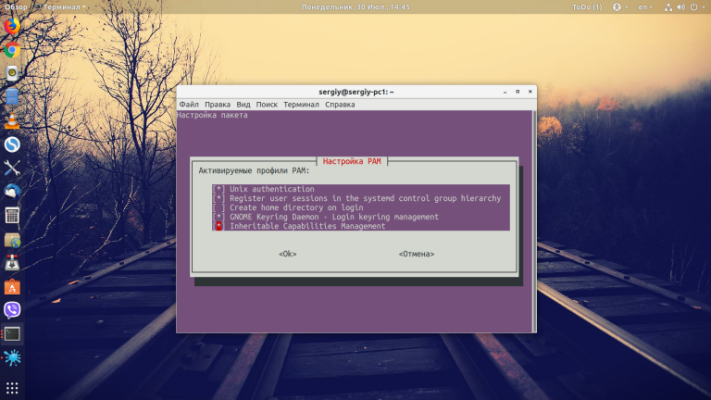
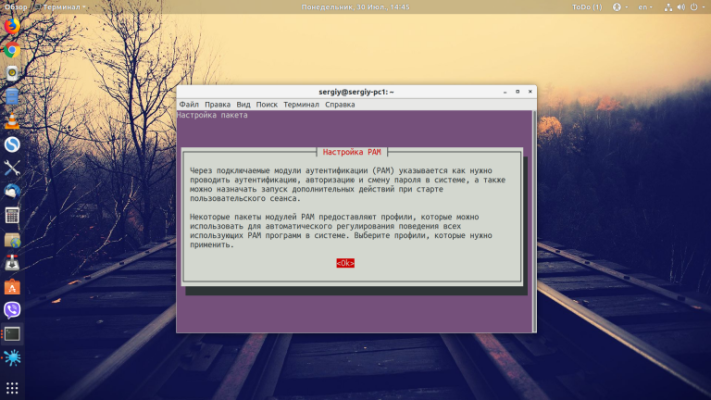
ls /etc/pam.d/You can start updating module settings by running as a superuser:
sudo pam-auth-updateOn the first step, you need to click Ok:
Then select the desired modules with the spacebar and arrows, switch with Tab to Ok and save.
Free disk space
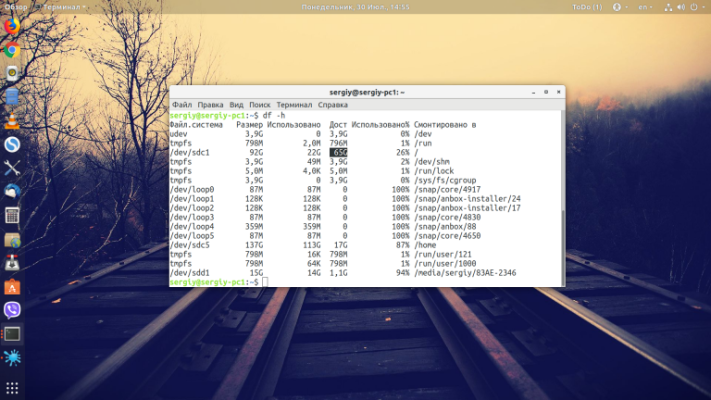
Naturally, the utility will not be able to change the password if there is no free space on the disk. Make sure there are at least a few hundred free megabytes on the root partition. This can be done using the command:
df -hTo see which files are taking up the most space and delete what you don't need, you can use ncdu:
sudo ncdu /If the utility is not installed, it can be installed using a package manager. The name of the package is the same as the command:
sudo apt install ncduThese are the main ways to solve this problem.