Email is more than just a familiar communication tool: behind every “send” and “receive” is a complex system of protocols that ensure messages are delivered anywhere in the world.
In 2025, we’re used to email “just working.” But even regular users benefit from understanding what happens behind the scenes: knowing the differences between SMTP, POP3, and IMAP helps you choose the right email client, configure it properly, or even set up your own mail server on a VPS.
 What is SMTP
What is SMTP
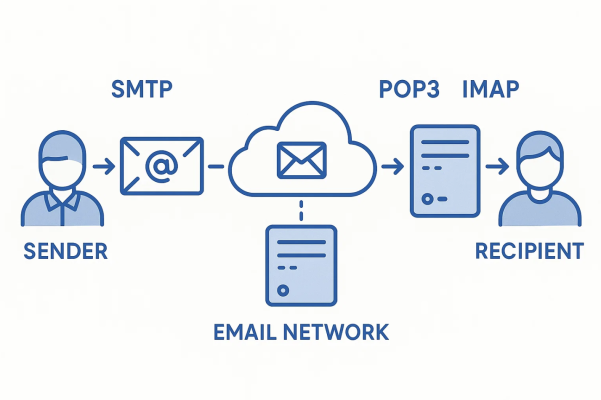
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is the protocol responsible for sending emails. The moment you click "Send," SMTP goes to work: it transfers your message from your email client to the recipient's server or an intermediate mail server.
Simply put, SMTP is like a courier delivering messages along a route. It doesn’t store emails or help you read them — it just transmits. SMTP works on a "point-to-point" basis: it receives a message and passes it along to the next node until it reaches the recipient.
What is POP3
POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3) is a protocol that allows emails to be downloaded directly from a mail server to a user’s device. The key feature of POP3 is that messages are typically deleted from the server after download and stored only locally — on your computer, phone, or tablet.
Advantages of POP3:
- Simplicity: no need for a constant internet connection after emails are downloaded.
- Saves space on the server: emails are stored on the user’s device.
Disadvantages of POP3:
- Inconvenient for multiple devices: if a message is downloaded to one device, it won’t appear on another.
- Risk of data loss if the device fails.
In 2025, POP3 still has its niche — where internet connections are unstable, or where email is checked from a single device, such as in some legacy corporate environments.
How SMTP, POP3, and IMAP differ
Let’s compare these protocols side by side:
|
Protocol |
Main purpose |
Where it’s used |
Key features |
|
SMTP |
Sending emails |
When you click “Send” |
Transfers messages between servers |
|
POP3 |
Receiving emails |
Checking mail from a single device |
Downloads emails to device and removes from server |
|
IMAP |
Receiving emails |
For access across multiple devices |
Stores emails on server and syncs status |
The key distinction: SMTP is only responsible for sending messages, while POP3 and IMAP handle receiving them. Your choice between POP3 and IMAP depends on how and where you want to manage your email.
By the way, if you’re renting a VPS and plan to deploy your own mail server, promo code HELLO gives a 15% discount on any VPS at THE.Hosting — simply apply it during checkout.
Which protocol to choose
Choosing a protocol depends on how you use email.
Everyday users:
If you check email only on a single device (like your home laptop), POP3 is enough — it’s simple and lightweight.
Freelancers and active users:
If you read email on multiple devices — phone, laptop, tablet — IMAP is the better choice. It keeps everything synchronized and up to date across all your devices.
Companies and teams:
For business email, IMAP works best: it ensures reliable sync and keeps emails stored on the server, which is critical for teamwork. SMTP is used alongside for sending mail.
Conclusion
In everyday life, most people don’t think about how email works — it “just delivers messages.” But understanding the differences between SMTP, POP3, and IMAP can help you choose the best way to work, especially if you manage your own mail server or plan to use a VPS.
Modern hosting providers support all these protocols by default. Even if you’ve never heard these terms, they quietly work in the background to ensure your emails are delivered reliably and are accessible across all your devices.