Tmux (Terminal Multiplexer) is a command line utility for managing multiple terminals within a single window. It allows users to run multiple programs in a single terminal, split a terminal window into multiple panes, and group multiple panes in a single window. Moreover, tmux allows the user to save terminal sessions and resume them at any time. Tmux is very useful for managing remote servers and for creating more efficient multitasking environments in Linux.
How to install
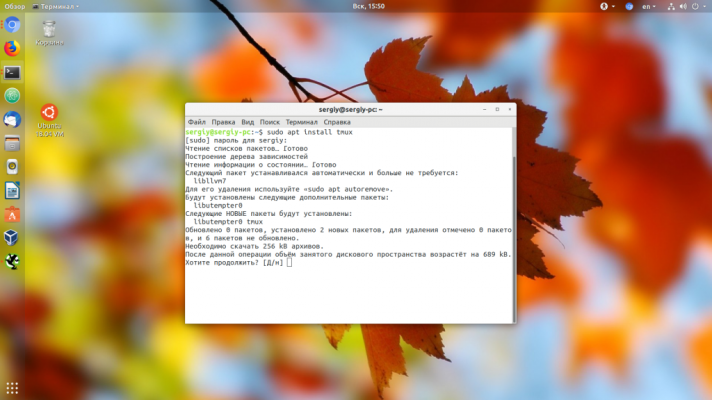
To install Tmux on most distributions, the system's standard package manager is used. For example, to install Tmux on Ubuntu/Debian, you can use the following command in a terminal:
sudo apt install tmuxTo install on CentOS/RHEL/Fedora, you can use the command:
sudo dnf install tmuxAfter installation, you can run Tmux with the command tmux in terminal.
If you need a more up-to-date version of Tmux, you can build and install it yourself from source. To do this, you must first install the necessary dependencies (at least the header file packages) and then compile and install the package. The command to download the Tmux source code:
wget
https://github.com/tmux/tmux/releases/download/3.2a/tmux-3.2a.tar.gzNext, you need to unzip the archive and navigate to the directory with the Tmux source code:
tar zxvf tmux-3.2a.tar.gz
cd tmux-3.2aNext, follow the instructions in the README file to compile and install Tmux. Typically these are:
./configure
make
sudo make installOnce installed, you can run Tmux with the tmux command in the terminal.