Docker is a popular containerization program. Containers are a standard unit of software that packages the code and all its dependencies so that the application can be run quickly and reliably on different operating systems and computing environments.
In technical terms, a container is a running process that is isolated from other processes and has access to computer resources. Next, let's look at installing Docker in Debian 11 and running the first application.
Adding a repository
There are two ways to install, using the standard Debian repositories or the official Docker repository. The Debian repositories do not contain the most recent version, so let's consider installing from the official Docker repository.
Before adding the repository, you need to update the package list by running the command:
$ sudo apt update
Also install additional packages that are needed to work with remote repositories. To install these packages you need to run the command:
$ sudo apt -y install ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release
Next, download and add the PGP key from the repository. To do this, run the command:
$ curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg
To add the repository you need to run the command:
$ echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/debian $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
Install the package
To install the package, first you need to update the package lists so that a new repository appears in the system. To do this, simply run the command:
$ sudo apt update Finally, you can install additional packages. The installation is done using the command:
Finally, you can install additional packages. The installation is done using the command:
$ sudo apt -y install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
The word ce in the package name docker-ce stands for community, which means that the free version (aka community version) will be installed. Now you know how to install docker debian.
Startup and autoloading
After installation, it will be disabled by default. To start the program you need to run the command:
$ sudo systemctl start docker
In order for it to run with the operating system it must be added to the autoloader using the command:
$ sudo systemctl enable docker
Add user
By default, only the root user can use and execute its commands in the terminal. If you execute any command from a normal user, the terminal will display the following error:
Got permission denied while trying to connect to the Docker daemon socket at unix:///var/run/docker.sock: Get "http://%2Fvar%2Frun%2Fdocker.sock/v1.24/containers/json": dial unix /var/run/docker.sock: connect: permission denied
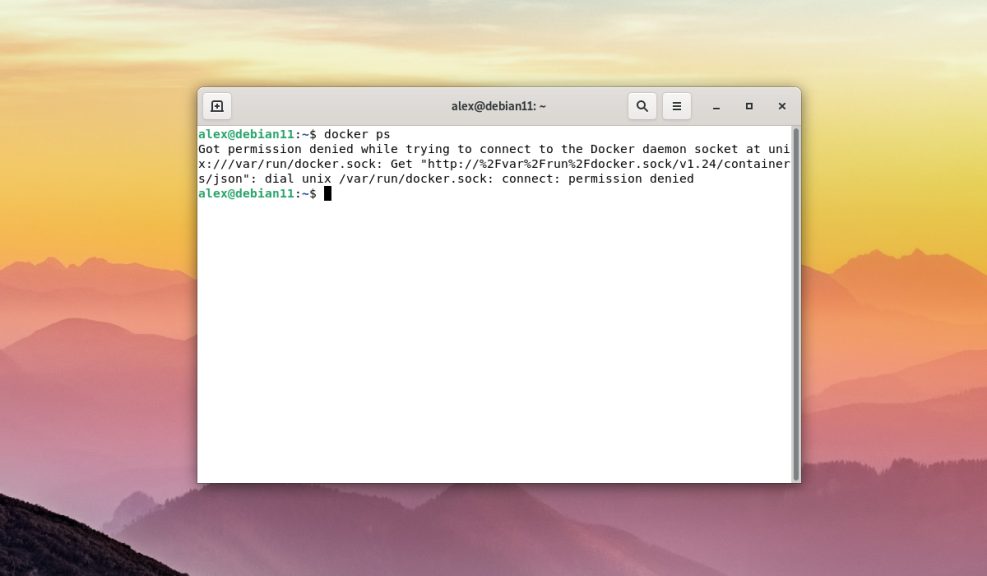
To run the command as a normal user and without using the sudo command, you must add the user to the docker group. The docker group is created automatically during installation. However, if for some reason it is not created automatically, it must be created manually by executing the following command:
$ sudo groupadd dockerNext, to add the current user to the docker group, you must execute:
$ sudo usermod -aG docker $USER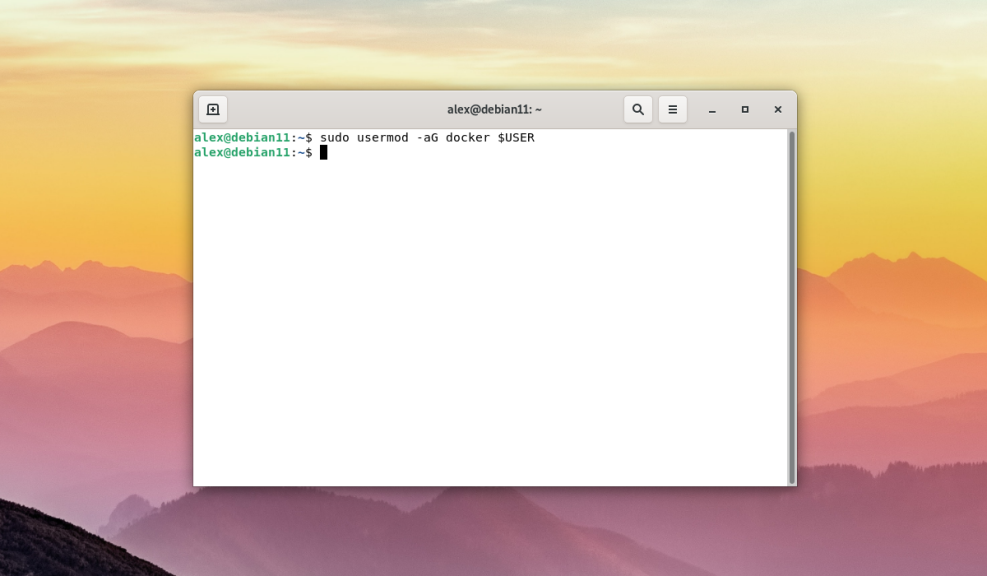
The $USER variable means that the current user, on behalf of whom the session is started, will be added to the docker group. This variable is present in all modern Linux distributions. It should also be noted that the docker group grants privileges equivalent to those of the root user.
After adding a user, it is necessary to re-login in the system and only then you can run any Docker command for testing. As an example, the docker ps command was run which displays a list of running containers:
$ docker ps
As you can see in the screenshot above it was executed without errors and on behalf of a normal user.
Running a container with HELLO-WORLD
To fully test Docker, you can download a test image from hello-world for validation. To do this, you need to execute:
$ docker run hello-world
The docker run command will download the program image from the docker hub online repository, the official default software image storage registry from Docker, and automatically run it. The example outputs the phrase Hello from Docker! which means that the image was successfully downloaded and run.