You can view the space occupied by a specific folder on your Linux disk using the file manager. You need to open the file properties. But there the information is not displayed in full, and often you need details. With the help of the utility ls to get detailed information is not possible. But the utility du for these purposes will work perfectly. Next we will tell you how to see the size of a folder in Linux using du. For this purpose, we will look at two examples of its use
How to find out the size of a directory
First we will tell you how to get information about a certain folder, with or without taking into account its attachments. Then we will move on to the subfolders in a particular directory. At the same time we will mention some useful nuances of working with du, for example, the ability to sort the data.
Specific folder
Let's take the Downloads folder as an example. The command to output its size looks like this:
$ sudo du -sh /home/root-user/DownloadsThe result will be its disk space:
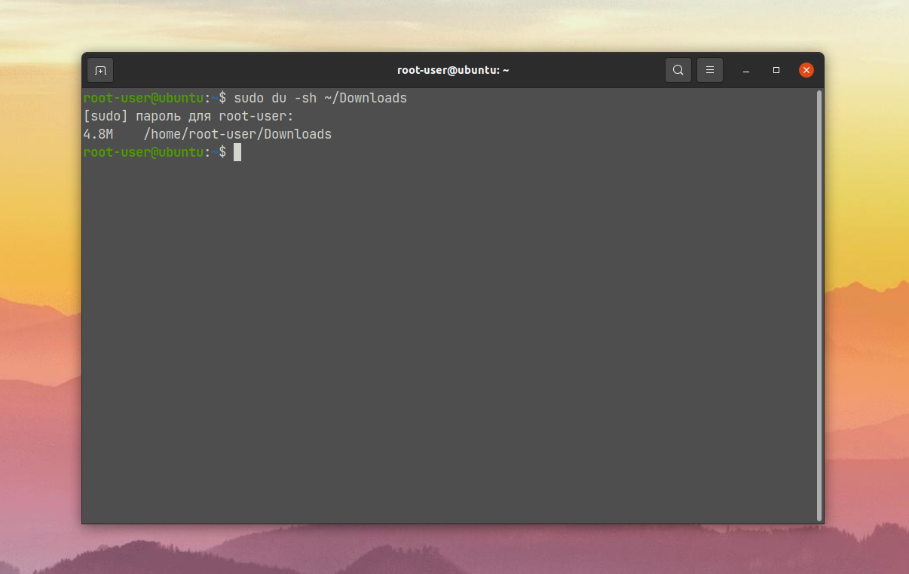
To get a better understanding of the command, let's briefly go through the options involved:
-s- output only the size of the folder itself, without subfolders.-h- output information in the usual form. We are talking about units of measurement (K - kilobytes, M - megabytes, etc.).
You can also view the total size of only the files in the folder, without taking into account the contents of subfolders. The-S option is used for this purpose:
$ sudo du -sSh /home/root-user/Downloads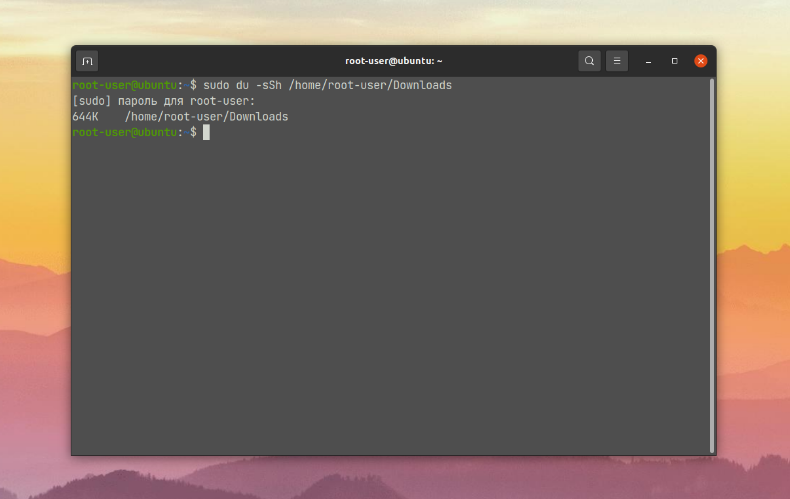
As you can see, it is very easy to find out the size of a folder.
Folders in a directory
A second useful scenario for using the du utility is to output the size of all subfolders in a particular directory, without taking into account the files inside. Again, let's take the Downloads directory as an example. Here is the command we need:
$ sudo du -h /home/root-user/Downloads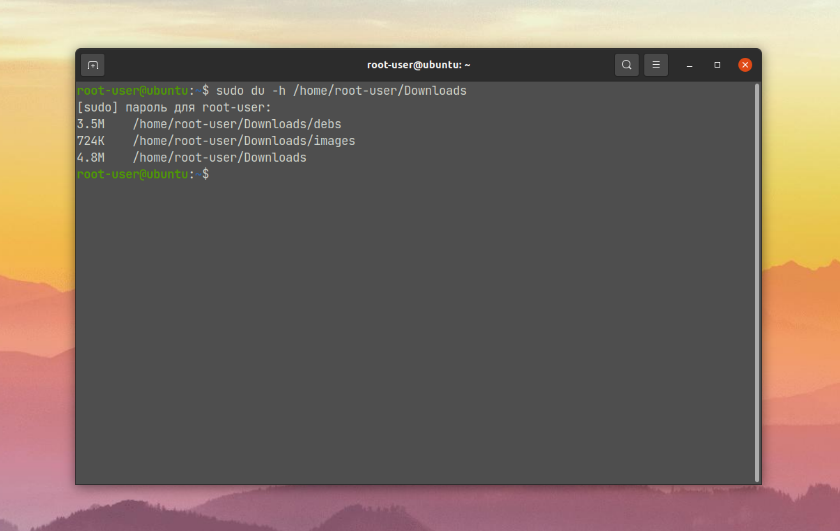
As a result of its execution, the terminal will display first the size of the subfolders and then the size of the folder itself. Using the --max-depth option you can set the maximum nesting depth. If you are interested only in the folder itself, the depth is 0, if you are also interested in its subfolders, the depth is 1 or more:
$ sudo du -h --max-depth=1 /home/root-user/Downloads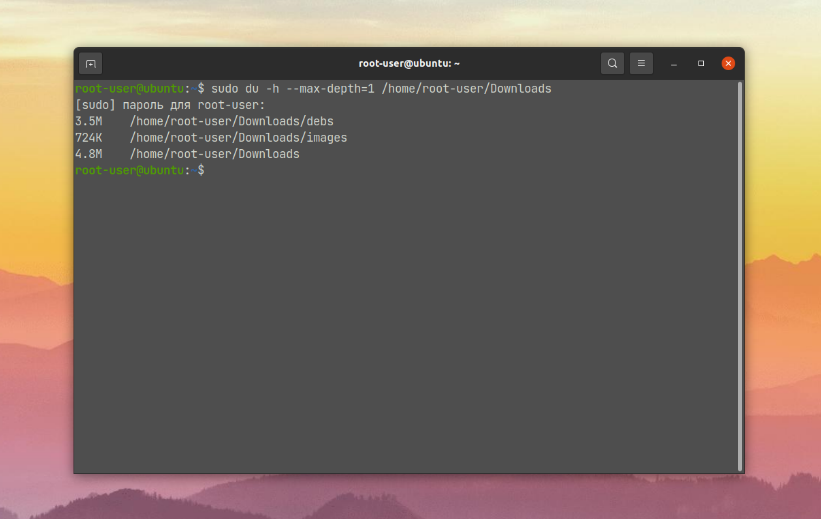
This is useful when the directory is very large and you need to limit the scope of the du utility.
You can also see the size of the folder itself and all files inside it, including subfolders. For these purposes, you should additionally set the -a option:
$ sudo du -ah /home/root-user/Downloads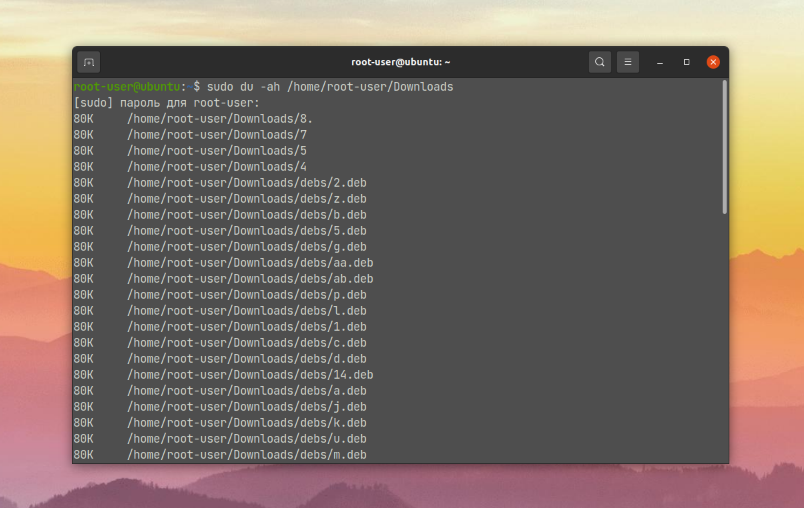
If the output data is too large, in some situations it makes sense to sort them by size. To do this, add | sort -rh after the path to the directory in the main command:
$ sudo du -ah /home/root-user/Downloads | sort -rh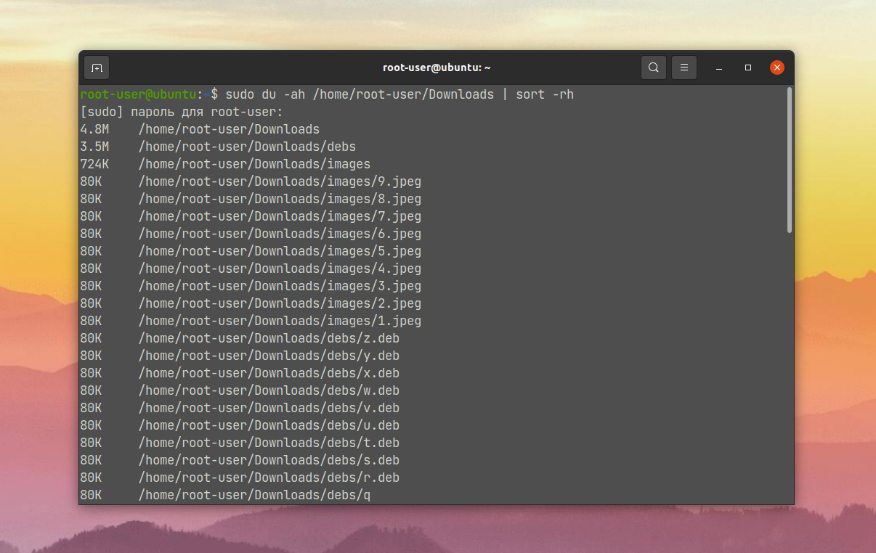
Now you know how to see the size of a folder in Linux and its attachments using the du utility.