The chmod command in the Linux operating system and other UNIX-like systems is used to change access rights to files and directories. Permissions determine what operations are allowed for a particular file or directory, such as reading, writing, and executing.
What does chmod allow you to do?
You can use the chmod command to change permissions for a file's owner, group, and other users. Permissions can be set as numeric values or character modes.
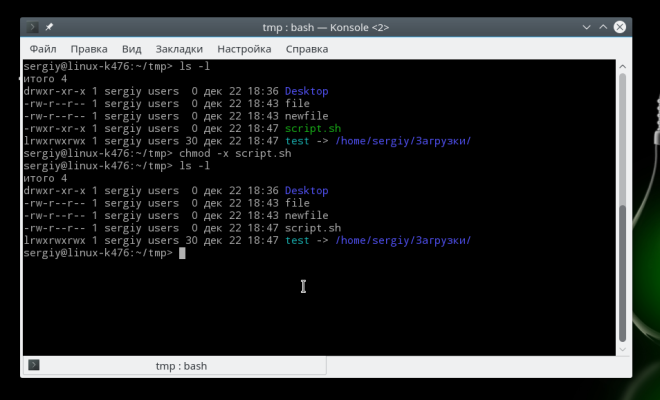
This is how permissions are changed: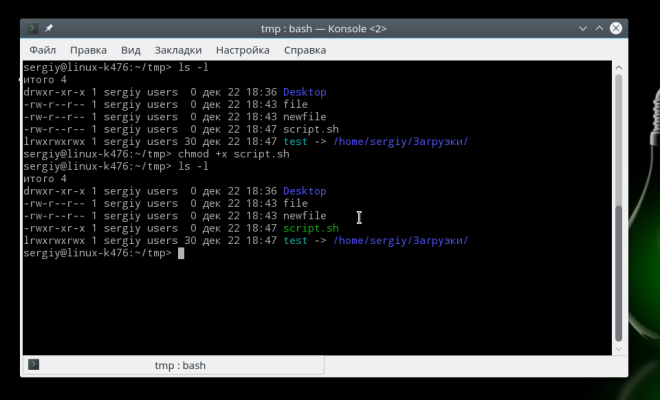
To remove the flag executable use the -x option:
For example, to set read, write, and execute permissions for the owner of a file, and read-only for the group and the rest of the users, you can use the following command:
chmod 755 filenamewhere"filename" is the name of the file or directory for which you want to change permissions.
How to install chmod
To install chmod, you need to run the following command in a terminal:
chmod <access rights> <file or directory name>where:
<accessrights> is a numeric value or character mode that specifies the required access rights. Numeric values can be from 0 to 7, where each digit corresponds to a specific access right (4 - read, 2 - write, 1 - execute). Symbolic modes consist of a combination of letters"r","w" and"x" for different categories of users (owner, group, others).
<fileor directory name>- the path to the file or directory for which you want to change permissions.
Examples of using the chmod command:
- Set read, write, and execute permissions for the owner of the file, and read-only for the group and other users:
chmod 755 filename - Set read and execute permissions for the file owner and group, and read-only for other users:
chmod 554 filename - Set read/write permission for the file owner and group, and read-only for all other users:
chmod 664 filename - Set execute permission for all users:
chmod +x filename - Set read and write permission for the file owner:
chmod u+rw filename - Set run permission for the group and other users:
chmod go+x filename
The chmod command cannot be removed because it is a built-in command in most UNIX and Linux operating systems. However, you can change the permissions on a file or directory back to the default values if that is what you want to do.
To reset the permissions on a file or directory back to the default values, you can use the chmod command with the appropriate numeric values or character mode. For example, to set permissions to 644 for a file, you can run the following command:
chmod 644 filenameThis will set read and write permissions for the owner of the file, and read-only for the group and other users.