In Linux OS, not only network interfaces, but also hard disks and SSD disks are represented by files in a special file system. There are several ways to see the list of Linux network interfaces, the easiest one is to see the contents of a folder in the file system. Next, let's look at all the basic ways to accomplish this task in a terminal or GUI.
List of interfaces
Ethernet network interfaces usually have a name that begins with the characters enp, for example, enp3s0. This name is used if your distribution uses systemd, otherwise the old naming system where names start with eth characters, such as eth0, will be used. Wireless network interfaces in most cases start with wlp or wlx when using systemd, e.g. wlp3s0. Without using systemd , the wireless interface name will start with wlan, for example wlan0. All other interfaces are usually virtual. One of the most basic virtual interfaces is lo. This is the local interface that allows programs to access this computer. Now let's look at a few ways to see a list of them.
File system
All network interface device files are located in the /sys/class/net folder. Therefore, you can view its contents:
$ ls /sys/class/net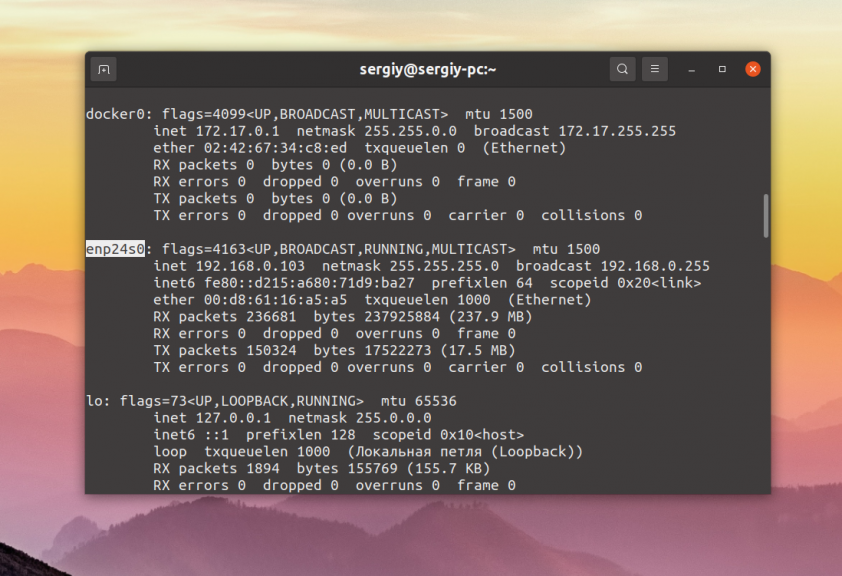
IFCONFIG utility
Theifconfig utility displays not only a list of network interfaces, but also information about them such as status, IP address, MAC address and other parameters. To display all interfaces, it is sufficient to execute the program without parameters:
$ ifconfig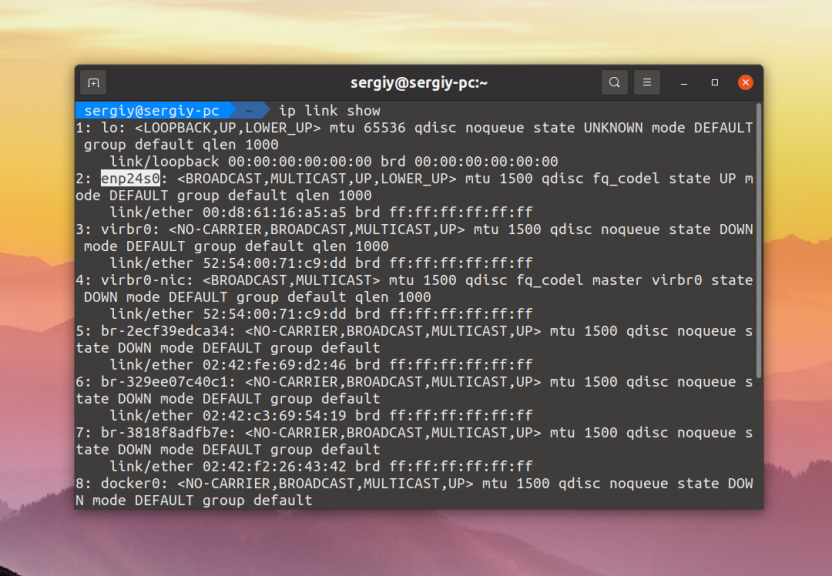
IP Utility
The ifconfig program has long been obsolete and has long been replaced by the ip utility. It combines the functions of such programs as ifconfig, route, brctl and others. You can view the list of devices using ip by running the command
$ ip link show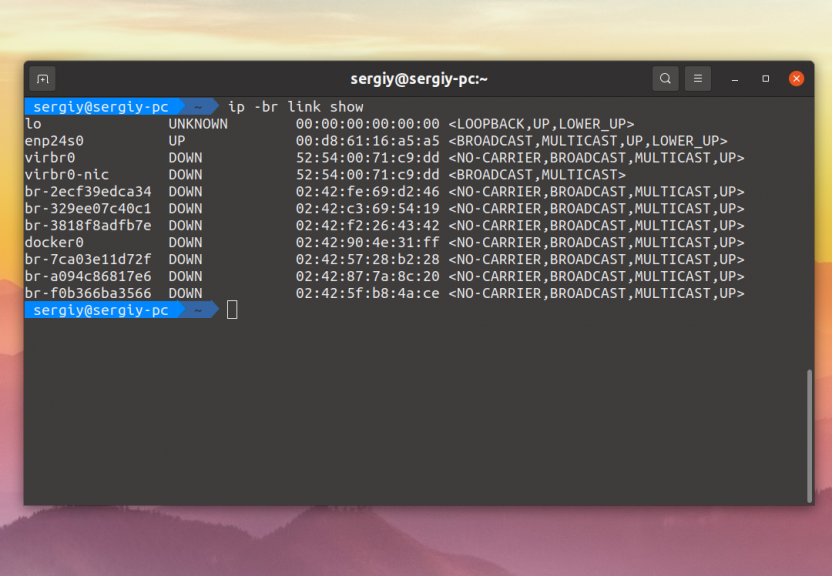
We see less information, only the device status, MTU and a few other parameters are shown. You can display the information in a more compact form by using the -br option:
$ ip -br link show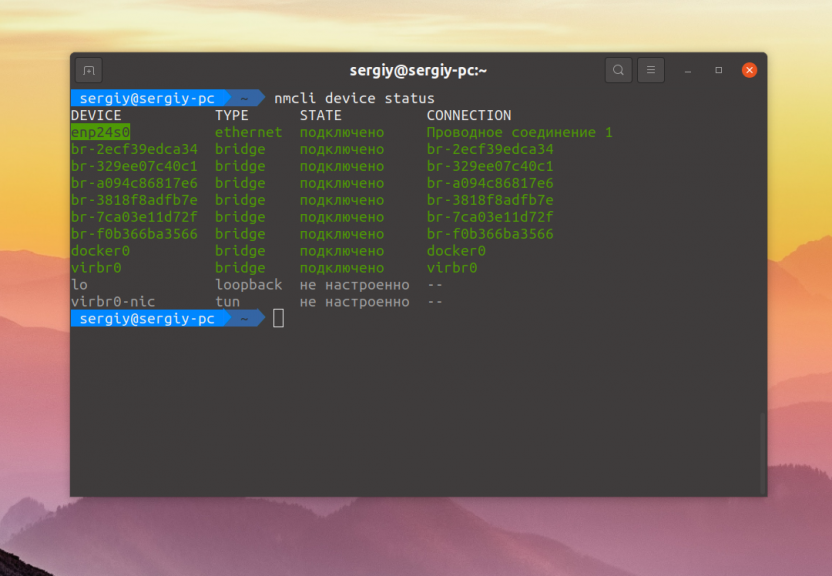
In this case all data is displayed in one line, the status, MAC address and a few more options are displayed.
NMCLI program
You can also view the information using the console firewall management utility - nmcli:
$ nmcli device status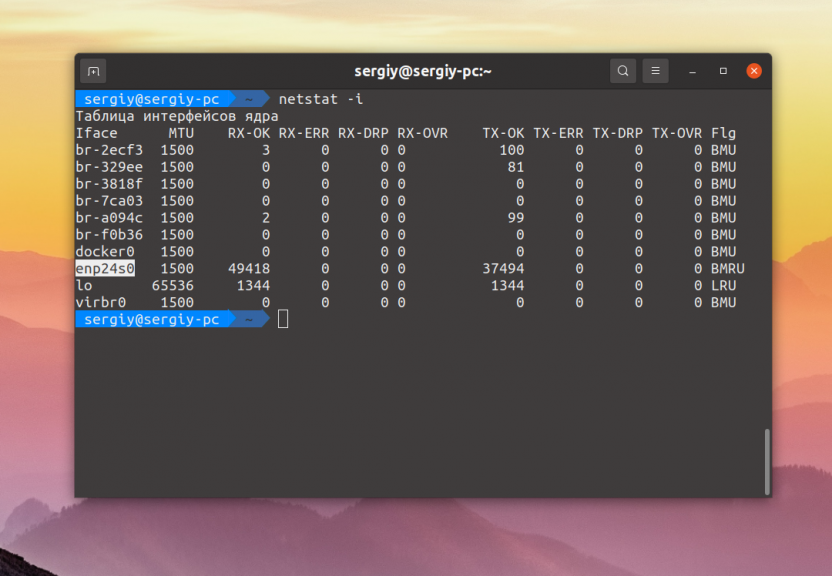
This displays the NetworkManager connection associated with a particular device, as well as its status.
NETSTAT program
The netstat program is also able to show network interfaces and statistics on transmitted data if the -i option is passed to it:
$ netstat-i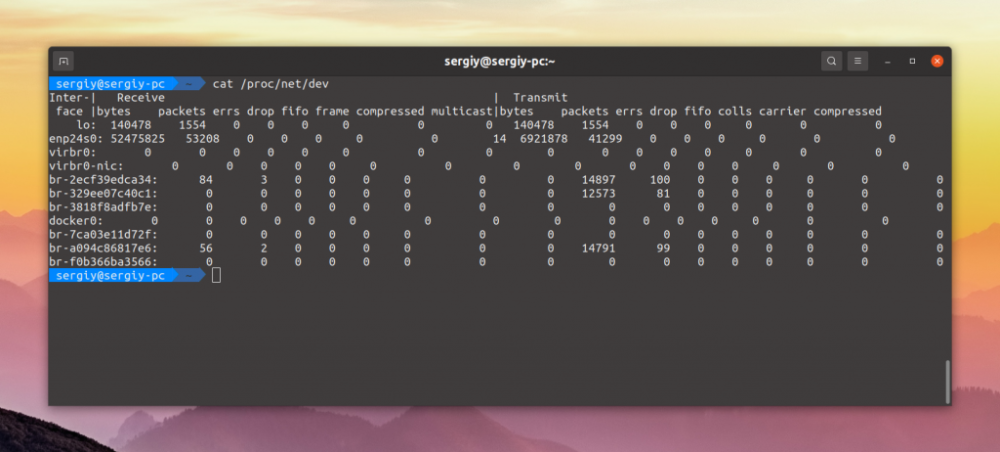
File /PROC/NET/DEV
The /proc/net/dev file also contains a list of all network interfaces and their usage statistics:
$ cat /proc/net/dev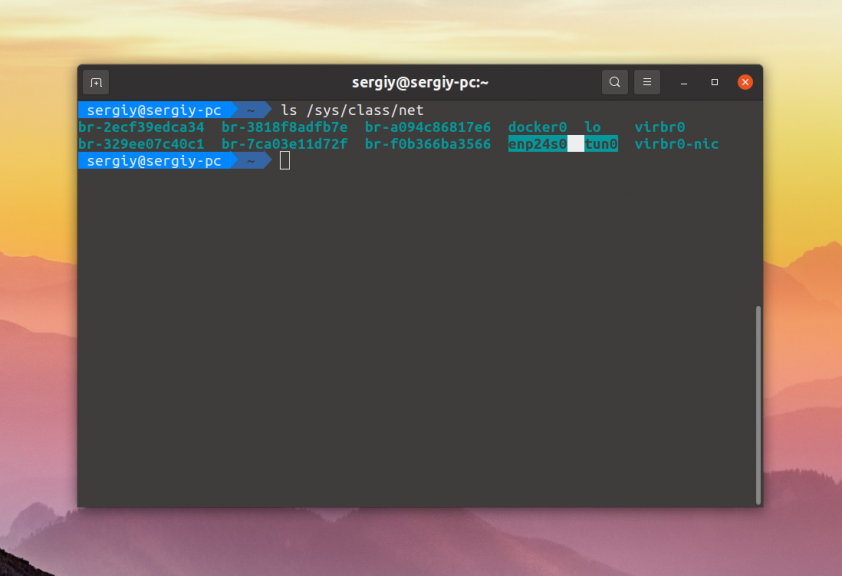
This is the end of this article.