Services in Linux can perform a variety of tasks such as network management, scheduler jobs, database jobs, data backup, security, and more. They are usually started at system startup and can run continuously until the system is shut down.
Why do I need to start a service?
Starting services in Linux is one of the fundamental processes in system management. Here are some reasons why you may want to start a service in Linux:
- Deploying Web sites: if you develop or host Web sites on your Linux server, you may need to run services such as Apache HTTP Server or Nginx to execute the Web server and serve Web pages to client requests.
- Running databases: when you have a database such as MySQL or PostgreSQL installed, you will need to run a database service to process queries and interact with the data.
- Mail handling: if your server sends or receives email, you can run services such as Postfix or Sendmail to ensure that emails are delivered.
- Network management: various network layer services such as DHCP, DNS or VPN can be run to ensure proper networking and communication.
Running a service in Linux
To start a service in Linux, you can use the systemctl start command. Here is what the general syntax of the command will be:
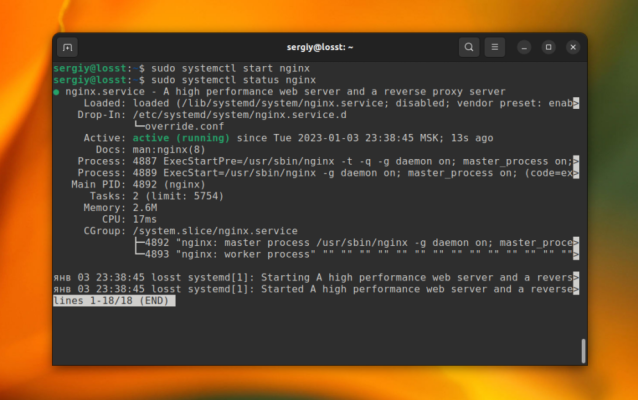
sudo systemctl start <service_name>Where <service_name> is the name of the service you want to start. Note that you will need superuser privileges to start the service, so use sudo before the systemctl start command.
Example:
sudo systemctl start apache2In this example, we are starting the Apache HTTP Server service. You can also start the service with the service command if your system does not use systemd:
sudo service <service_name> startExample:
sudo service nginx startThis starts the Nginx service. Remember that commands can vary depending on your Linux distribution, so make sure you use the correct command for your system.