Linux terminal is an obvious advantage of this OS family. With its help, it is easy to perform various actions in the OS. At the same time, the user can execute not only single commands, but also group them together. For this purpose, you can apply various operators to redirect input and control execution. If you know the hotkeys of the terminal, you will start working with it much more efficiently. Let's consider the main hotkeys that can be used in your work.
All useful keys in the Linux terminal
General commands
Ctrl+Alt+T- in Ubuntu-based distributions, this keyboard shortcut is used to open the terminal.Tab- this key is used to autocomplete in the terminal. All you have to do is type the beginning of some command, then press it and the command will suggest available options or end it if it is a single command.Ctrl+L- clear all terminal output.Ctrl+S- pause terminal output.Ctrl+Q- resume output if it was paused.Ctrl+C- sendSigIntsignal to the command to end it.Ctrl+Z- minimize the current command to background mode.
Command history
- Up and down arrows - used to move forward and backward through the command history.
Ctrl+r- can be used to search the history of commands.Ctrl+p- the previous command in the history of commands.Ctrl+n- the next command in the command history.Ctrl+g- if you are in the search mode, ends the search.Ctrl+o- execute the command found by the search.Alt+.- use the last word of the previous command.
Moving the cursor
Ctrl+a- move to the beginning of the line.Ctrl+e- move to the end of the line.Alt+b- move to the left by one word.Alt+f- move to the right by one word.Ctrl+b- move to the left by one character.Ctrl+f- move to the right by one character.Ctrl+xx- jump to the end or to the beginning of the line.
Editing
Ctrl+u- cut a line to the cursor position.Alt+Del- delete a word before the cursor.Alt+d- delete the word after the cursor.Ctrl+d- delete the character under the cursor.Ctrl+h- delete the character under the cursor.Ctrl+w- cut the word under the cursor.Ctrl+k- cut a line from the cursor position to the end of the line.Alt+t- swap the current word with the previous one.Ctrl+t- swap two characters in front of the cursor.Esc+t- swap two words before the cursor.Ctrl+y- paste what was cut.Alt+u- make upper case characters from the cursor position to the end of the current word.Alt+l- make lower case characters from the cursor position to the end of the word.Alt+c- change the character under the cursor to upper case and go to the end of the word.Alt+r- return the string to its original state.Ctrl+_- cancel the last action with the string.
The above commands work well in the bash shell. You can use other solutions, but then some terminal hotkeys may not work. It may also be the case that a certain combination will perform completely different actions.
The function of searching through the history of commands is considered to be very interesting and useful. Let's imagine a practical situation: you want to find the openvpn command and you know for sure that you have already executed it earlier. To solve the problem (search for it), we press Ctrl+R and start typing the command.
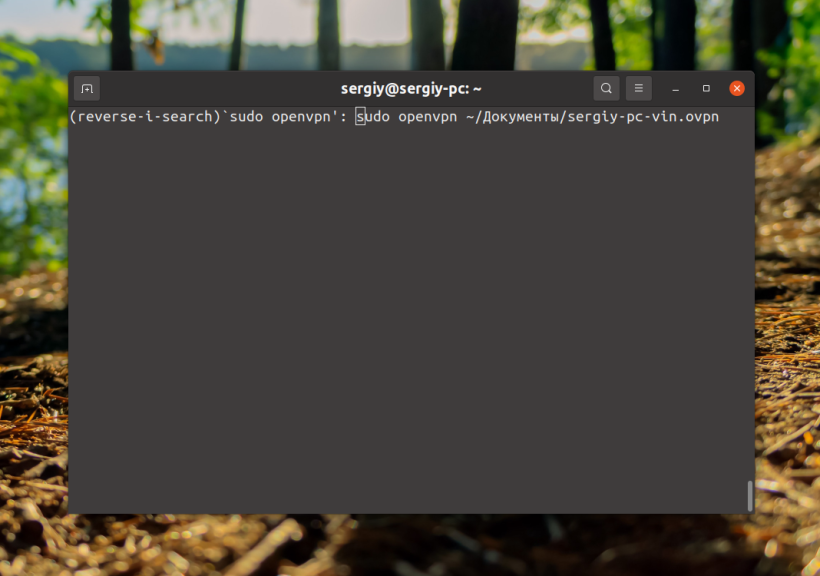
To execute the command, we need to press Enter or Ctrl+o. The Alt+r key combination is interestingly combined with this function. This way you find a certain command in the history and then modify it. By pressing these hotkeys, you return the command to its original state. In some cases this is necessary and useful. There are times when a command outputs information too quickly. Pause the output using the Ctrl+S keys. You can also do an experiment using this combination and the ping command:
Resume output by pressing Ctrl+S, and Ctrl+Q.