In 2000, a new standard of interaction between clients and servers was formed in the sphere of designing the architecture of program interfaces. It was called REST. The main initiator of this concept was Roy Fielding, one of the developers of the HTTP protocol. In today's world, REST API is becoming an increasingly popular tool for data exchange, providing effective interaction between all kinds of applications.
RESTful API is a list of principles and rules to organize the interaction between a client and a server. It allows developers to make easily changeable and scalable web applications. The basic idea behind REST is to represent resources that are accessible by unique URI identifiers, manipulating them using standard HTTP methods.
Fundamental concepts of REST APIs
What is an API? It is an interface that helps different programs communicate with each other. It defines how requests can be made and what responses can be received. API serves as the basis for integrating different systems and is a fundamental part of current application development.
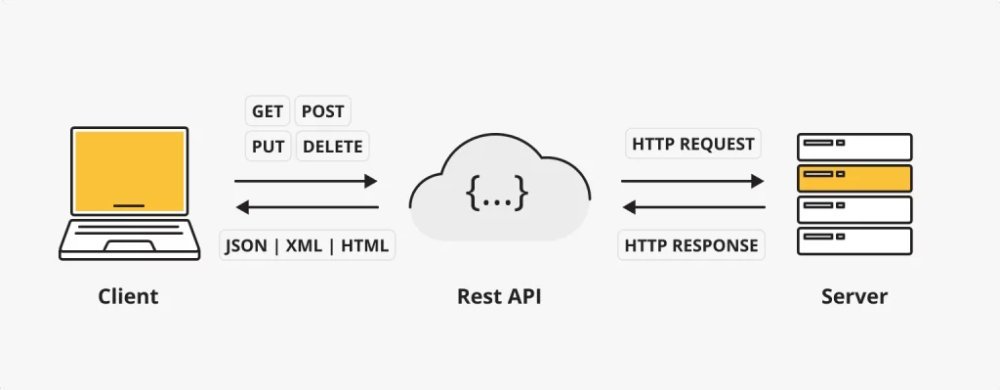
What is REST? It is an architectural style based on principles that make the application of web services convenient and easy to understand. It is based on HTTP protocols and uses standard methods, which will be broken down next. Each resource available through the API has its own unique identifier (URI), which facilitates access to it.
Principles of functioning of the REST API
The main ones are:
- Client-server. Separation of client and server parts facilitates independent development and change of both sides.
- Non-stationarity. The server does not save the state of client requests, which makes each request independent and self-sufficient.
- Caching. The ability to cache response data helps improve application performance by reducing the number of repeated requests to the server.
- Unified interface. It simplifies interaction and makes systems more predictable by using standard elements.
- Multi-tiered system. The architecture can consist of several layers, each responsible for specific aspects of the system. This increases security and manageability.
- On-demand code. This code is passed to the client to extend the capabilities of the application.
Advantages of REST API
Using this tool provides many pluses.
- Scalability. By separating client and server components, the application can easily scale.
- Flexibility. REST API supports a variety of programming languages and platforms, and allows integration of different systems.
- Performance. The use of caching improves response speed and reduces the load on the server.
- Security. The tiered system architecture enhances security by allowing critical resources to be isolated.
Despite the obvious advantages of REST, other technologies such as SOAP and GraphQL are also on the market. While the former is used in specific applications and provides its own features, the latter is developed by Facebook. GraphQL represents an alternative to REST. It is more suitable for large-scale projects.
How does the REST API function?

The process of client-server interaction can be broken down into several stages:
- Request sending. The client sends data to the server, formatting it according to the API documentation.
- Authentication. The server verifies the client's access right. In case of unsuccessful authentication, error 403 is returned.
- Request processing. After successful authentication the server receives the request, does the necessary manipulations and forms the response.
- Response return. The server sends a response to the client. It contains the command execution status and the requested data.
HTTP methods in REST API
Classic HTTP methods are used to work with resources:
GET: Used to retrieve data (for example,GET /citiesreturns a list of cities);POST: Used to create new resources (e.g.POST /istanbuladds a new cafe in Istanbul);PUT: Used to update existing resources (e.g.,PUT /citieschanges the list of cities);DELETE: Used to delete resources (e.g.DELETE /istanbuldeletes a cafe in Istanbul).
Each HTTP request returns a status code that indicates the result of the operation. A code starting with 2 indicates successful execution, while codes with 4 or 5 indicate errors.
REST API has become a standard in web service development, it provides users with a good tool for building flexible and scalable solutions. Its principles and benefits have contributed to its widespread popularity and use in a wide variety of applications, from building small web applications to complex distributed systems. In this extended introduction to the REST API, we will take a closer look at its main components, compare it with other technologies, discuss the use of REST in practice, and touch upon the prospects for its development.
Data types and formats when working with the REST API

When interacting with REST APIs, it is important to consider what data formats are used. The most common format is JSON (javaScript), which is easy to read and write, making it ideal for data transfer. However, other formats such as XML and HTML are sometimes used. The choice of data format may depend on the application requirements and developer preferences. JSON format supports complex data structures and provides economical bandwidth utilization, which is another advantage of REST API.
Authentication and authorization
Security is an important aspect when working with REST APIs. One of the authentication methods is the use of tokens. This provides secure access to protected resources. One of the most common methods is the use of JWT tokens. This method allows the client to access the API for a certain amount of time after authentication. The server does not need to store state, reinforcing the "no state" concept of REST.
In addition, such authentication can be augmented with OAuth 2.0. This adds an extra layer of security and simplifies integration with social media and other platforms.
REST APIs and mobile apps
With the growing popularity of smartphones, the REST API has become an important toolkit for developers building mobile applications. Using REST API allows applications to communicate with remote servers, receive and update data in real time. Therefore, it is possible to create complex applications: messengers, social networks and other software solutions that require high-speed access to information.
Example of REST API work in a practical application
For a better understanding of REST API, let's consider a hypothetical example of working with an API for library management. Suppose we have a RESTful API that allows us to perform the following actions:
- retrieve a list of books - the client can make a
GET requestto/booksto get information about all available books; - adding a new book - if necessary, the client can send a
POST requestto/bookswith data about a new book in JSON format; - correcting information about a book - to change information about an existing book, a
PUT requestto/books/{id}is used, where{id}is a unique identifier of the book; - deleting a book - a
DELETE requestcan be sent to the same URI to perform the operation.
These simple examples demonstrate how efficient resource management can be realized using REST APIs.
Tools and technologies for working with REST APIs
There are many features and libraries that facilitate collaboration. For example, Postman is a popular application that allows developers to send requests, perform testing, and analyze responses. Other tools, such as Swagger, allow you to document APIs and automatically generate code in a variety of programming languages.
In Python, you can use Requests libraries that provide a simple interface for sending HTTP requests and processing the responses. In javascript, especially within frontend development, use Fetch API or Axios.
Conclusion
REST API remains one of the most popular tools for client-server interaction. Its principles provide flexibility, scalability and ease of use, making it an ideal solution for most modern web applications. Despite the emergence of alternatives (GraphQL.)