As mentioned in previous articles, the DBMS can be installed from the official and developer repository. Regardless of this, during the installation, the program will ask several questions to be answered. Below we will tell you what and how to answer them.
Answering the DBMS questions
The first thing the program will ask the user is the root password. You will only need to specify it.
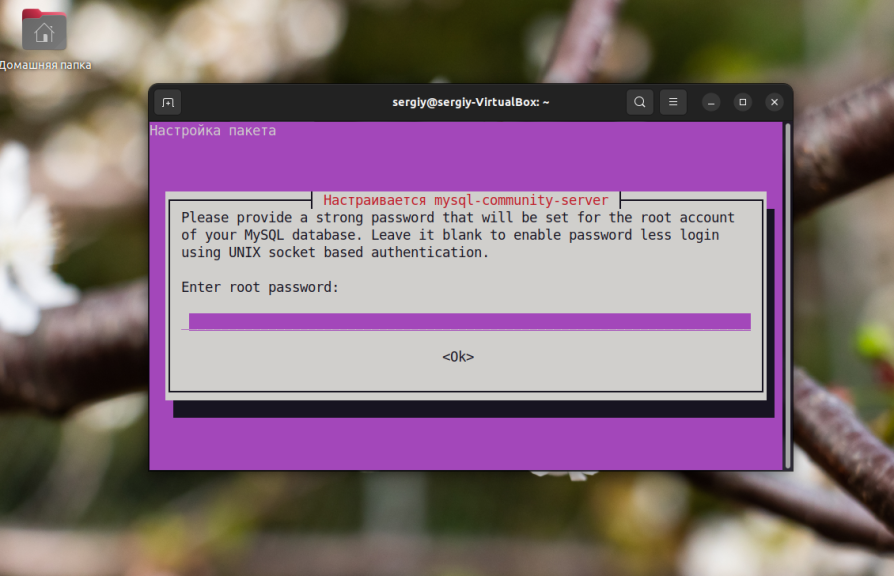
And then enter it again to confirm it:
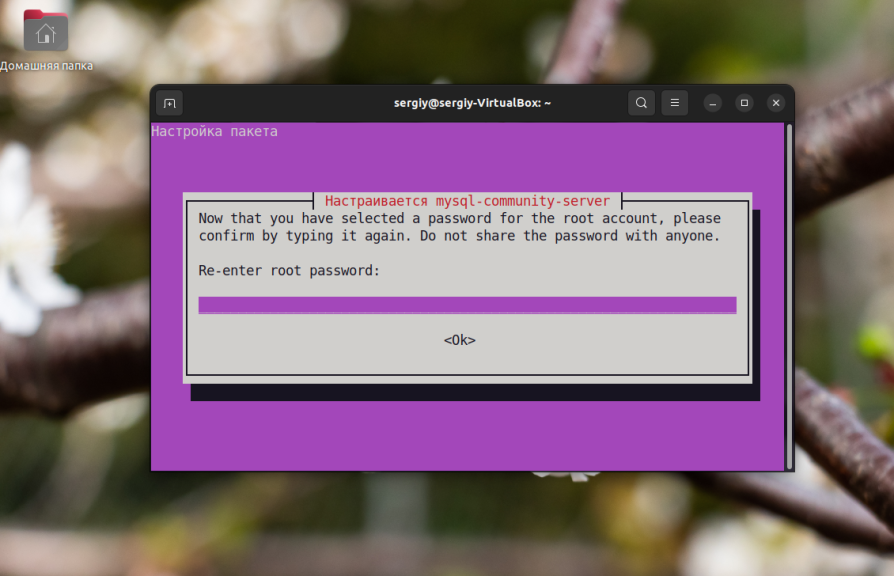
The user reserves the right to leave the password area blank, but in this case MySQL will use Unix authorization to log in when running the mysql client from the console (you will lose remote access). This will cause some more inconvenience in the future, so it is better not to do this and set the root password right away.
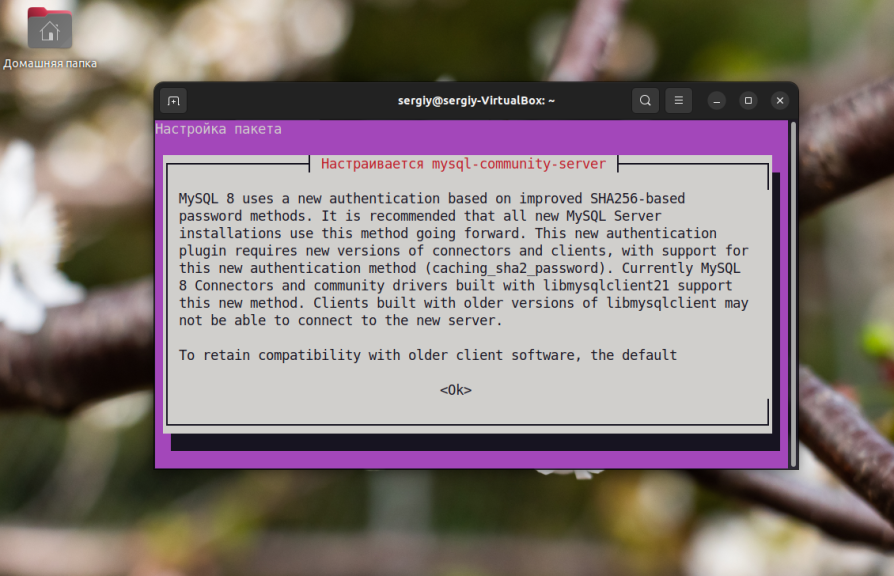
After that the program will warn you that MySQL is using a new method of authorization. This information can be found in the window that opens:
The installer will then prompt you to install the new authorization method or return the old one. The client libraries for MySQL in Ubuntu are already built to support the new method, so it can be left in place:
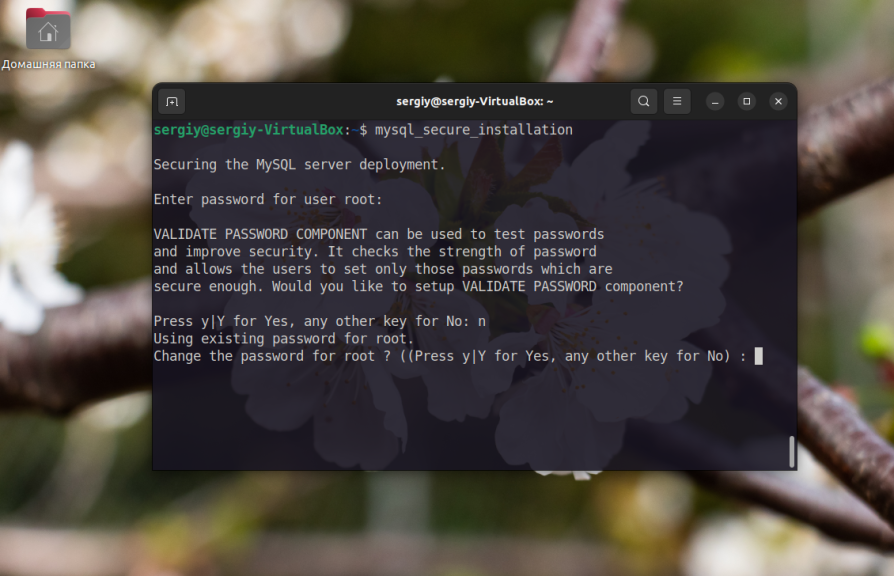
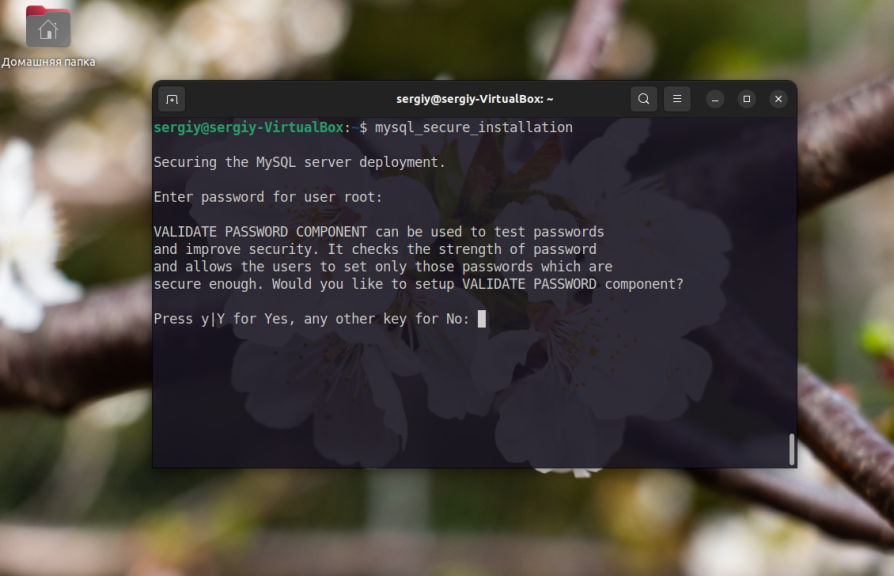
Once the installation is complete, you need to execute the mysql_secure_installation command (to help protect the MySQL server). If you did set a password during the MySQL installation phase, you can run the command without sudo. If the password was not set, the first thing to do is to set the code for the root user.
mysql_secure_installationHave you entered and set the root password? Next, the command will prompt you to enable the MySQL password validation plugin. Do not enable it if you have no idea what it is and what it is for. In short, the plugin will prevent installation of too simple passwords for MySQL users. At this point, answer n:
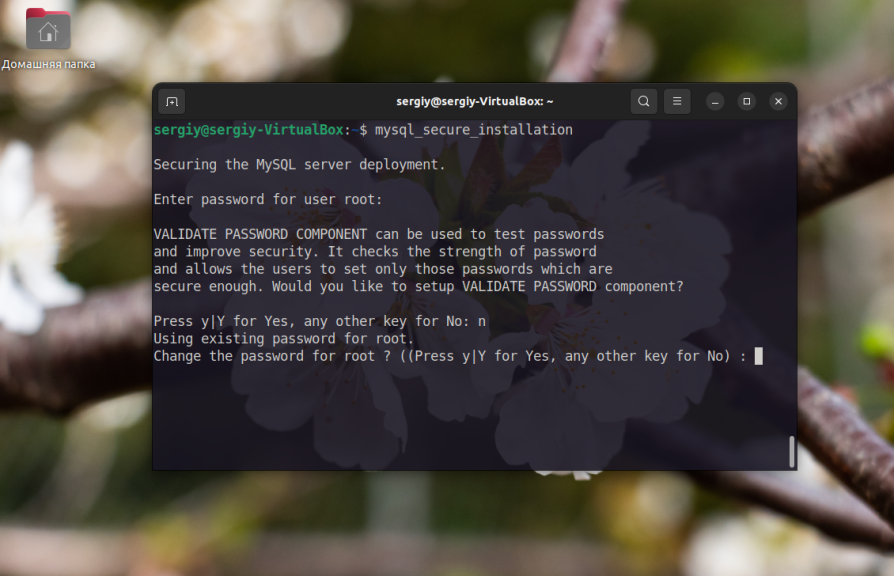
Next, the utility will ask if the root password should be changed. Here you can also answer n, since you have already set the password earlier:
Answer all subsequent questions from the program in the affirmative:

Using this configuration principle, you will not be able to apply only sudo to connect to mysql from the console. You can try, but you will get an Access Denied error. To connect to MySQL using the console client, enter the root password that was set earlier:
mysql -u root -p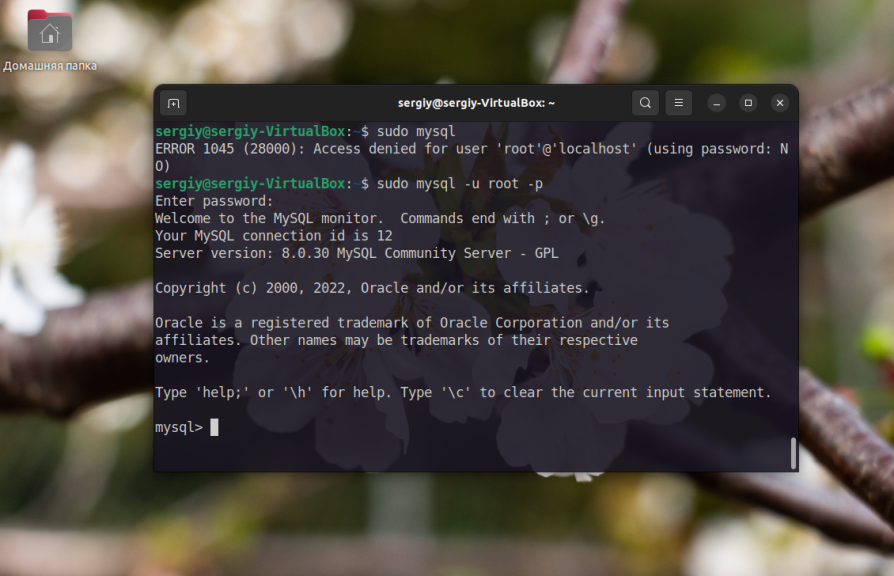
This completes the configuration instructions.
Rent mysql vps